Heart Attack
 The role of the heart is to pump oxygen-rich blood to every living cell in the body. In order to achieve its goal, it must continuously beat for a person’s entire lifespan. Because of its vital role, a non-beating heart always results in death. The human heart beats approximately 80,000 to 100,000 a day and pumps almost 2,000 gallons of blood. This means that in a person’s life lasting 70 to 90 years, the heart beats approximately two to three billion times and pumps 50 to 65 million gallons of blood. Because the heart is so essential for human sustenance, it is made up of a muscle different from skeletal muscle that allows it to constantly beat.
The role of the heart is to pump oxygen-rich blood to every living cell in the body. In order to achieve its goal, it must continuously beat for a person’s entire lifespan. Because of its vital role, a non-beating heart always results in death. The human heart beats approximately 80,000 to 100,000 a day and pumps almost 2,000 gallons of blood. This means that in a person’s life lasting 70 to 90 years, the heart beats approximately two to three billion times and pumps 50 to 65 million gallons of blood. Because the heart is so essential for human sustenance, it is made up of a muscle different from skeletal muscle that allows it to constantly beat. Systole: Stage when the ventricles of heart are contracting resulting in blood being pumped out to the lungs and the rest of the body.
Systole: Stage when the ventricles of heart are contracting resulting in blood being pumped out to the lungs and the rest of the body.
 Commonly known as a heart attack, myocardial infarction occurs when the blood supply to part of the heart is interrupted. Heart attacks are most often caused by the blockage if a coronary artery following the rupture of a plaque that had formed on the artery wall. If left untreated, the restriction in blood supply, known as ischemia, can cause the heart tissue to become damaged or even die.
Commonly known as a heart attack, myocardial infarction occurs when the blood supply to part of the heart is interrupted. Heart attacks are most often caused by the blockage if a coronary artery following the rupture of a plaque that had formed on the artery wall. If left untreated, the restriction in blood supply, known as ischemia, can cause the heart tissue to become damaged or even die.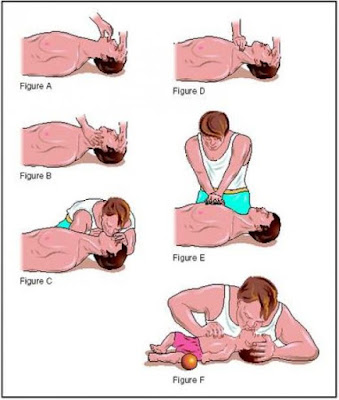 * Begin by ensuring that the patient’s airway is open. Lift his chin with one hand, and with the other tilt his head backwards. This would open up the airway, relieving it of any obstruction caused by the tongue or epiglottis.
* Begin by ensuring that the patient’s airway is open. Lift his chin with one hand, and with the other tilt his head backwards. This would open up the airway, relieving it of any obstruction caused by the tongue or epiglottis.
Adults should take steps to control heart disease risk factors whenever possible.
The Human Heart
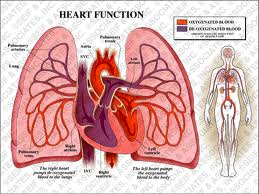
The heart is a muscular organ responsible for pumping oxygenated blood through the blood vessels with repeat, rhythmic contractions. The human heart is located in the center of your chest, slightly offset to the left side. The average adult's heart is 9-12 ounces, or about the size of a clenched fist. It consists of four chambers, the two upper atria and the two lower ventricles, and four valves which open and close to let the blood flow through the heart in only one direction.
The right side of the heart collects oxygen-depleted blood and pumps the blood into the lungs so that carbon dioxide can be dropped off and fresh oxygen picked up. The left side of the heart collects the freshly-oxygenated blood and pumps it out to the body.
 The role of the heart is to pump oxygen-rich blood to every living cell in the body. In order to achieve its goal, it must continuously beat for a person’s entire lifespan. Because of its vital role, a non-beating heart always results in death. The human heart beats approximately 80,000 to 100,000 a day and pumps almost 2,000 gallons of blood. This means that in a person’s life lasting 70 to 90 years, the heart beats approximately two to three billion times and pumps 50 to 65 million gallons of blood. Because the heart is so essential for human sustenance, it is made up of a muscle different from skeletal muscle that allows it to constantly beat.
The role of the heart is to pump oxygen-rich blood to every living cell in the body. In order to achieve its goal, it must continuously beat for a person’s entire lifespan. Because of its vital role, a non-beating heart always results in death. The human heart beats approximately 80,000 to 100,000 a day and pumps almost 2,000 gallons of blood. This means that in a person’s life lasting 70 to 90 years, the heart beats approximately two to three billion times and pumps 50 to 65 million gallons of blood. Because the heart is so essential for human sustenance, it is made up of a muscle different from skeletal muscle that allows it to constantly beat.In order for the heart to deliver oxygenated blood to all cells, blood is pumped through arteries. Veins bring deoxygenated blood cells to the lungs, which then are oxygenated, and then sent back to heart. In this way, a continuous cycle is formed of the heart pumping oxygenated blood and deoxygenated blood out to their designated destinations, and therefore the heart maintains the circulatory system.
The heartbeat is made up of systole and diastole, which are the two stages of a heartbeat.
 Systole: Stage when the ventricles of heart are contracting resulting in blood being pumped out to the lungs and the rest of the body.
Systole: Stage when the ventricles of heart are contracting resulting in blood being pumped out to the lungs and the rest of the body.- Thick, muscular walls of both ventricles contract.
- Pressure rises in both ventricles, causing the bicuspid and tricuspid valves to close. Therefore, blood is forced up the aorta and the pulmonary artery.
- The atria relax during this time. The left atrium receives blood from the pulmonary vein, and the right atrium from the vena cava.
Diastole: Stage when the ventricles of the heart are relaxed and not contracting. During this stage, the atria are filled with blood and pump blood into the ventricles.
- Thick, muscular walls of both ventricles relax.
- Pressure in both ventricles falls low enough for bicuspid valves to open.
- The atria contract, and blood is forced into the ventricles, expanding them.
- The blood pressure in the aorta is decreased, therefore the semi-lunar valves close.
Because the brain relies on a steady supply of oxygenated blood, the heart is one of the most vital organs in a person's body. Some of the disease and conditions that put your heart health at risk include:
- Arrhythmia
- High cholesterol
- Congenital heart disease (heart defects)
- Diabetes
- Heart attack
- Heart failure
- High blood pressure
- Metabolic syndrome
- Obesity
- Peripheral artery disease (PAD)
- Stroke
Leading a healthy lifestyle can help reduce your risk for heart disease and stroke. Eating a nutritious diet, managing your weight and exercising regularly will help promote heart health.
 Commonly known as a heart attack, myocardial infarction occurs when the blood supply to part of the heart is interrupted. Heart attacks are most often caused by the blockage if a coronary artery following the rupture of a plaque that had formed on the artery wall. If left untreated, the restriction in blood supply, known as ischemia, can cause the heart tissue to become damaged or even die.
Commonly known as a heart attack, myocardial infarction occurs when the blood supply to part of the heart is interrupted. Heart attacks are most often caused by the blockage if a coronary artery following the rupture of a plaque that had formed on the artery wall. If left untreated, the restriction in blood supply, known as ischemia, can cause the heart tissue to become damaged or even die.- Chest pain (typically down the left arm or left side of the neck, and often described as a sensation of tightness, pressure, or squeezing)
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Palpitations
- Sweating
- Anxiety

Women may not have as many of these typical symptoms, and also commonly report:
- Shortness of breath
- Weakness
- Feeling of indigestion
- Fatigue
Surprisingly, the onset of heart attack is usually gradual, developing over several minutes. If you or someone you love is experiencing the above-listed symptoms, call emergency services immediately to help prevent damage to the heart.
If someone you know or indeed if you suspect you are having a heart attack, timely and sensible first-aid can make a major difference in the final outcome. First call for immediate help. If you are alone, dial an ambulance or your physician. The next best thing to do is to sit quietly or lie down if you are feeling faint. Breathe slowly and deeply. And chew on an aspirin tablet as it thins the blood and improves the outcome significantly.
Prop the person up in a half-reclining position. Loosen his clothing. Open all the windows of the room to allow fresh air inside. If the patient is conscious and a chewable aspirin tablet is available, ask him to crunch it. Here are some other points to keep in mind: raise the person’s legs as this would divert vital blood to his brain and remove the pillow from underneath his head. If the person faints or has lost consciousness, there is no time to lose. Administer cardio-pulmonary resuscitation (CPR).
 * Begin by ensuring that the patient’s airway is open. Lift his chin with one hand, and with the other tilt his head backwards. This would open up the airway, relieving it of any obstruction caused by the tongue or epiglottis.
* Begin by ensuring that the patient’s airway is open. Lift his chin with one hand, and with the other tilt his head backwards. This would open up the airway, relieving it of any obstruction caused by the tongue or epiglottis.* Next move on to mouth-to-mouth respiration. Keep the patient’s airway in the open position. Pinch his nose, place a fresh handkerchief in between and give two full breaths while maintaining an airtight seal with your mouth on his mouth. Look at his chest for simultaneous chest expansion.
* Now, feel for his carotid pulse. It lies in the groove by the side of the Adam’s apple. If no pulsation can be felt, begin cardiac massage. For this, locate the notch where the bottom rims of the two halves of the rib cage meet in the middle of the chest. Place the heel of one hand here. Now place your other hand on the top of the first one. Bring your shoulders directly over the patient’s breastbone and keeping your arms straight, depress down a good four to five cm. Then relax the pressure. But do not remove your hands. Compress again. Keep doing this at the rate of 80 to 100 compressions a minute. After every 15 compressions, give two mouth-to-mouth breaths.
* Keep at it, until expert medical assistance arrives.
Adults should take steps to control heart disease risk factors whenever possible.
- If you smoke, quit. Smoking more than doubles the chance of developing heart disease.
- Keep blood pressure, cholesterol, and diabetes in good control and follow your doctor's orders.
- Lose weight if obese or overweight.
- Get regular exercise to improve heart health. (Talk to your doctor before starting any new fitness program.)
- Eat a heart-healthy diet. Limit saturated fats, red meat, and sugars. Increase your intake of chicken, fish, fresh fruits and vegetables, and whole grains. Your health care provider can help you tailor a diet specific to your needs.
- Limit the amount of alcohol you drink. One drink a day is associated with reducing the rate of heart attacks, but two or more drinks a day can damage the heart and cause other medical problems.


A heart attack occurs when blood flow to a part of your heart is blocked for a long enough time that part of the heart muscle is damaged or dies. Your doctor calls this a myocardial infarction.
Most heart attacks are caused by a blood clot that blocks one of the coronary arteries. The coronary arteries bring blood and oxygen to the heart. If the blood flow is blocked, the heart is starved of oxygen and heart cells die.
A hard substance called plaque can build up in the walls of your coronary arteries. This plaque is made up of cholesterol and other cells. A heart attack can occur as a result of plaque buildup.
- The plaque can develop cracks or tears. Blood platelets stick to these tears and form a blood clot. A heart attack can occur if this blood clot completely blocks oxygen-rich blood from flowing to the heart. This is the most common cause of heart attacks.
- The slow buildup of plaque may almost block one of your coronary arteries. A heart attack may occur if not enough oxygen-rich blood can flow through this blockage. This is more likely to happen when your body is stressed (for example, by a serious illness).
- When you are resting or asleep
- After a sudden increase in physical activity
- When you are active outside in cold weather
- After sudden, severe emotional or physical stress, including an illness
Cardiogenic shock is a state in which the heart has been damaged so much that it cannot supply enough blood to the organs of the body. This condition is a medical emergency.
A heart attack is a medical emergency. If you have symptoms of a heart attack, call 108 or your local emergency number right away.
- DO NOT try to drive yourself to the hospital.
- DO NOT DELAY. You are at greatest risk of sudden death in the early hours of a heart attack.

Chest pain is the most common symptom of a heart attack. You may feel the pain in only one part of your body, or it may move from your chest to your arms, shoulder, neck, teeth, jaw, belly area, or back.
- A tight band around the chest
- Bad indigestion
- Something heavy sitting on your chest
- Squeezing or heavy pressure
The pain usually lasts longer than 20 minutes. Rest and a medicine called nitroglycerin may not completely relieve the pain of a heart attack. Symptoms may also go away and come back.
- Anxiety
- Cough
- Fainting
- Light-headedness, dizziness
- Nausea or vomiting
- Palpitations (feeling like your heart is beating too fast or irregularly)
- Shortness of breath
- Sweating, which may be very heavy
Some people (the elderly, people with diabetes, and women) may have little or no chest pain. Or, they may have unusual symptoms (shortness of breath, fatigue, weakness). A "silent heart attack" is a heart attack with no symptoms.
A doctor or nurse will perform a physical exam and listen to your chest using a stethoscope.
- The doctor may hear abnormal sounds in your lungs (called crackles), a heart murmur, or other abnormal sounds.
- You may have a rapid pulse.
- Your blood pressure may be normal, high, or low.
A troponin blood test can show if you have heart tissue damage. This test can confirm that you are having a heart attack.
Coronary angiography is often done right away or when you are more stable. You may also have tests such as an electrocardiogram (ECG).
electrocardiogram (ECG)
- This test uses a special dye and x-rays to see how blood flows through your heart.
- It can help your doctor decide which treatments you need next.
Other tests to look at your heart that may be done while you are in the hospital:
- Echocardiography
- Exercise stress test
- Nuclear stress test
You will most likely first be treated in the emergency room.
- You will be hooked up to a heart monitor, so the health care team can look at how your heart is beating.
- The health care team will give you oxygen so that your heart doesn't have to work as hard.
- An intravenous line (IV) will be placed into one of your veins. Medicines and fluids pass through this IV.
- You may get nitroglycerin and morphine to help reduce chest pain.

Abnormal heartbeats (arrhythmias) are the leading cause of death in the first few hours of a heart attack. These arrythmias may be treated with medications or cardioversion.
Angioplasty is a procedure to open narrowed or blocked blood vessels that supply blood to the heart. Usually a small, metal mesh tube called a stent is placed at the same time.
- Angioplasty is often the first choice of treatment. It should be done within 90 minutes after you get to the hospital, and no later than 12 hours after a heart attack.
A stent is a small, metal mesh tube that opens up (expands) inside a coronary artery. A stent is often placed after angioplasty. It helps prevent the artery from closing up again.
You may be given drugs to break up the clot. It is best if these drugs are given within 3 hours of when you first felt the chest pain. This is called thrombolytic therapy.
Some patients may also have heart bypass surgery to open narrowed or blocked blood vessels that supply blood to the heart. This procedure is also called open heart surgery.
- Keep your blood pressure, blood sugar, and cholesterol under control.
- Don't smoke.
- Eat a heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and low in animal fat.
- Participate in regular Physical activity.
- Go for regular health check ups.
- Use other supplement as folic acid and garlic under supervision.
- Try to reduce fat, not more 30 calories should come from fat a day
- Get plenty of exercise, at least 30 minutes a day, at least 5 days a week (talk to your doctor first).
- Get checked and treated for depression.
- Limit yourself to no more than one drink a day for women, and no more than two drinks a day for men.
- Stay at a healthy weight.
Coconut, eggs, Amla, dry fruits, cardomom(elaichi), cinnamon, honey, black grape juice, pomegranate juice, turmeric in food, cloves, garlic, dry ginger, coriander seeds, cow milk (talk to your doctor first).
- Boil dry ginger in water and make thick syrup. Consume this syrup twice a day after food to reduce heart pain, to reduce cholestrol, indigestion, stomache ache and cough.
- Collect lotus seeds from lake and make powder. Take 5gms of this powder with 1 spoon honey to strengthen heart and reduce asthma and also hiccups.
- Dry ginger 20 gms powder and boil in 300 ml water till it boils down to 100 ml and then drink it every morning on empty stomach
- Amla (indian gooseberry) powder 100gm and candy sugar 100 gms. Mix them and store. Twice a day after food have 5 gms of this powder
- Mix cow milk with cooked brown rice and have during nights instead of yogurt or curd
- Never have cold water or any cold beverage or wash face with cold water after sex or dinner or after coming into home from hot sun

Subscribe to:
Post Comments
(
Atom
)















Top Cancer Hospitals in Bangalore that have facilities to carry out biopsies, blood tests, MRI's, ultra sound and x-rays. Choose hospitals that are well prepared to complete transplants and also find live organ donors to facilitate quick transplant procedures.
ReplyDelete